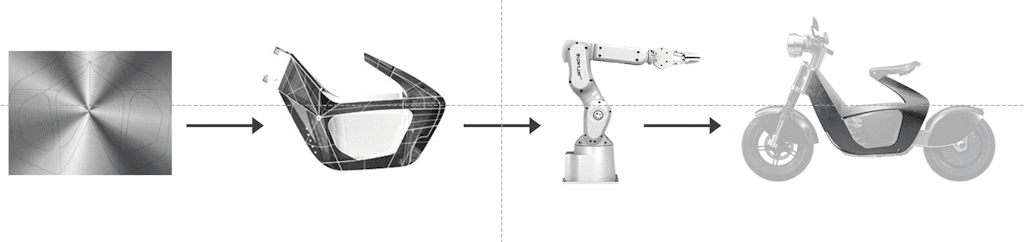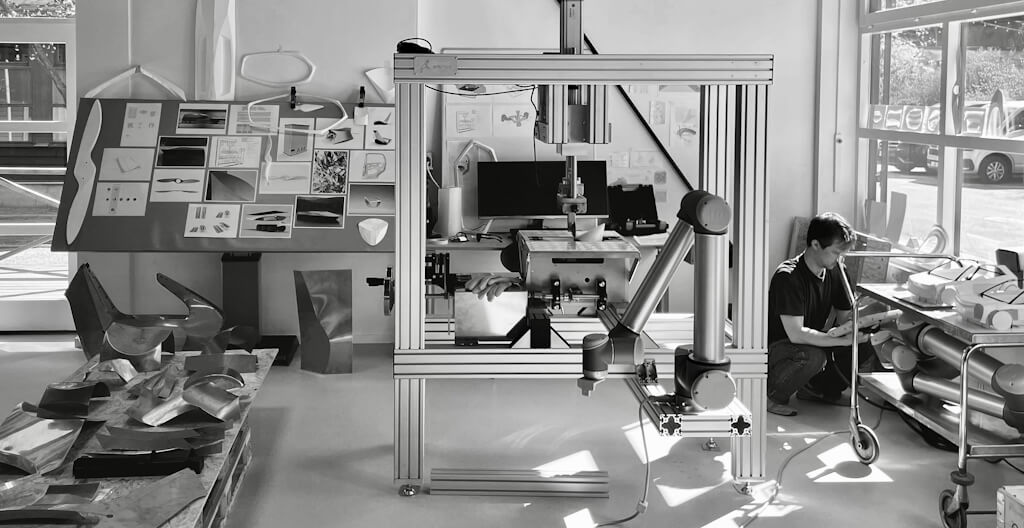
The Swedish startup renowned for its origami-inspired approach to design and manufacturing, STILFOLD, has joined forces with Linköping University in Sweden to optimise the performance of its sustainable manufacturing technology using artificial intelligence.
Text & images by STILFOLD
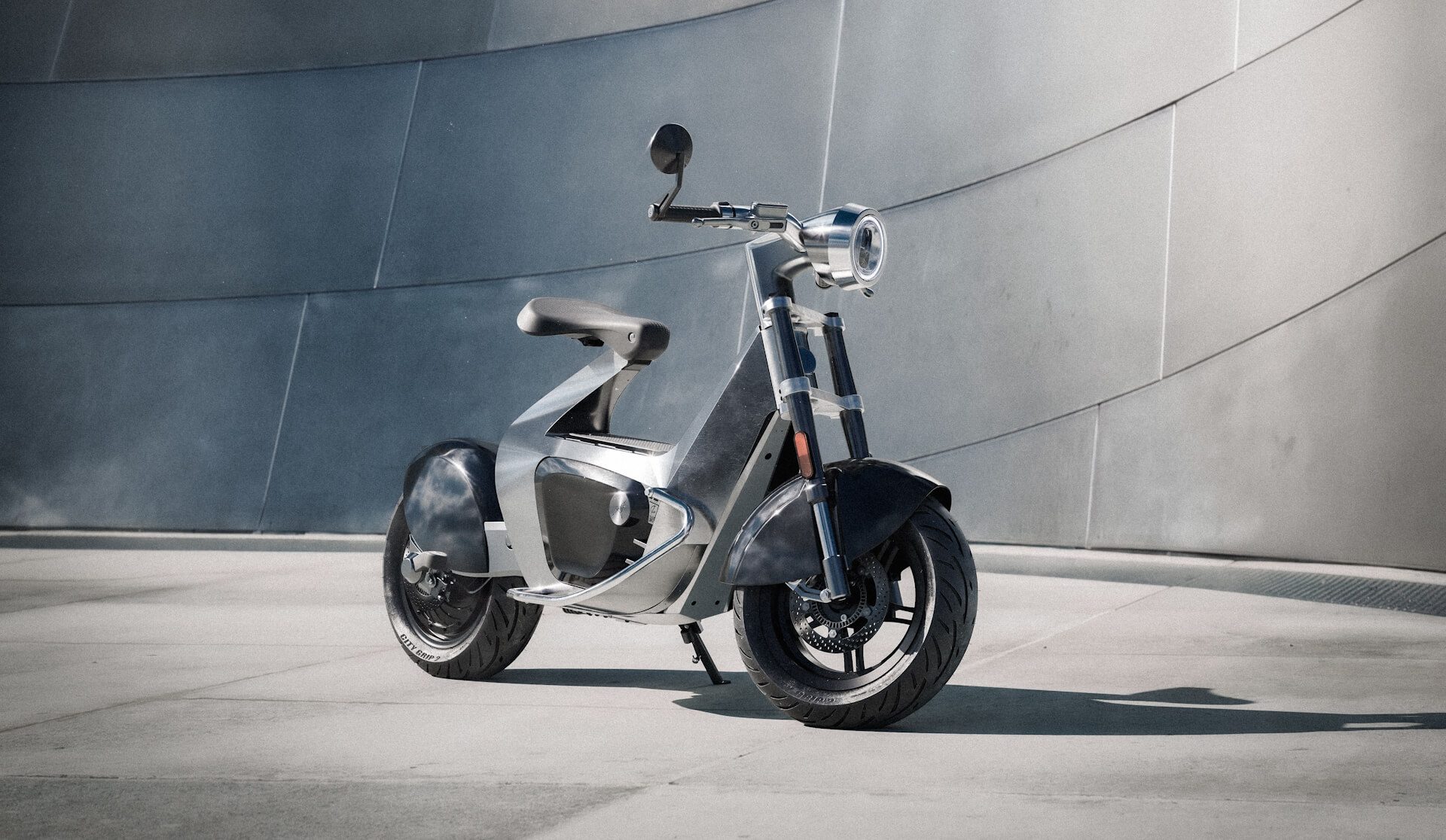
The STILFOLD technology, dubbed “industrial origami”, involves the use of robotic arms to fold flat sheet metal over curves to form light and sustainable new structures using minimal component parts. The technology is currently being used to build the chassis of a light electric motorcycle called the STILRIDE 1, the world’s first climate-neutral car (in collaboration with Polestar), and to develop greener urban mobility infrastructure (in collaboration with Alstom).
Currently, STILFOLD’s proprietary “STILWARE” software enables designers to create folding instructions for any given design, before it is folded into shape. Now, STILFOLD will work with partners at Linköping University to optimise and automate elements of the process using AI, making the process more efficient and reliable.
They will create an AI model which can predict the optimal sequence of folds which should be used to produce any given shape. They will also work to enhance STILFOLD’s existing technology infrastructure to optimise how its robots are programmed to create folds.
Based on data
STILFOLD will train its models on new and existing data from the (stainless) steel industry, as well as proprietary STILFOLD data including the outcomes of different folding patterns, as well as how different materials respond to different folding techniques. The team will use a combination of digital twin technology, reinforcement learning techniques and detailed material models embedded in physics-informed neural networks (PINN) to deliver their advanced computational tools.
The new technology will make it even easier for designers to use STILFOLD’s curve-folding technology to build robust and ever more complex shapes.
Earlier this year, the first STILFOLD machine was sold to Georgia Tech’s School of Civil and Environmental Engineering in the USA, where it is being used by students and academics for education and innovation.
Swedish innovation
The initiative is being backed by Vinnova, Sweden’s innovation agency, which will be injecting 10 million SEK into the project as part of its Advanced Digitalization programme.
Jonas Nyvang, CEO and co-founder at STILFOLD commented: “AI can help us optimise the entire STILFOLD process over time, and help us find ways to improve and possibly change the process depending on the material used. It’s a very exciting project for us. We want to push the boundaries of how AI can be used in the manufacturing and mobility industries going forward.”
“To have a chance of reaching future climate goals, we must take giant leaps, especially in these sectors. We possess a technology that could be such a giant leap for a large part of the industry, but it also requires completely new ways of thinking about tools and technology.”
ODEN-AI Project
The project, operating under the working name ODEN-AI (Optimized Digitalization for Environmentally NeutrAI Industrialization), is scheduled to run until 2026. Besides Linköping University and STILFOLD, Outokumpu (STILFOLD’s steel partner) and Jernkontoret – an organisation which collects and compiles data on the Swedish steel industry – will contribute expertise to the project.
Vinnova has also granted STILFOLD a research project which will see the company test the use of recycled aluminium in its products. The project is part of the “LIGHTer” strategic innovation initiative coordinated by Research Institutes of Sweden AB (RISE). The programme is aimed at bolstering the expertise and capabilities of Swedish enterprises, enabling them to evolve into highly specialised suppliers of lightweight solutions for Swedish industry.
STILFOLD has been awarded a further prestigious EIT Manufacturing Grant of EUR 816,000 to further develop their technology. The grant is dedicated to projects that are pushing the boundaries of “Environmentally Sustainable Manufacturing through Circular Business Models and New Technologies”.

About this Tech Article
This tech article appeared in Stainless Steel World, April 2024 magazine. To read many more articles like these on an (almost) monthly basis, subscribe to our magazine (available in print and digital format) – SUBSCRIPTIONS TO OUR DIGITAL VERSION ARE NOW FREE.
Every week we share a new Featured Story with our Stainless Steel community. Join us and let’s share your Featured Story on Stainless Steel World online and in print.